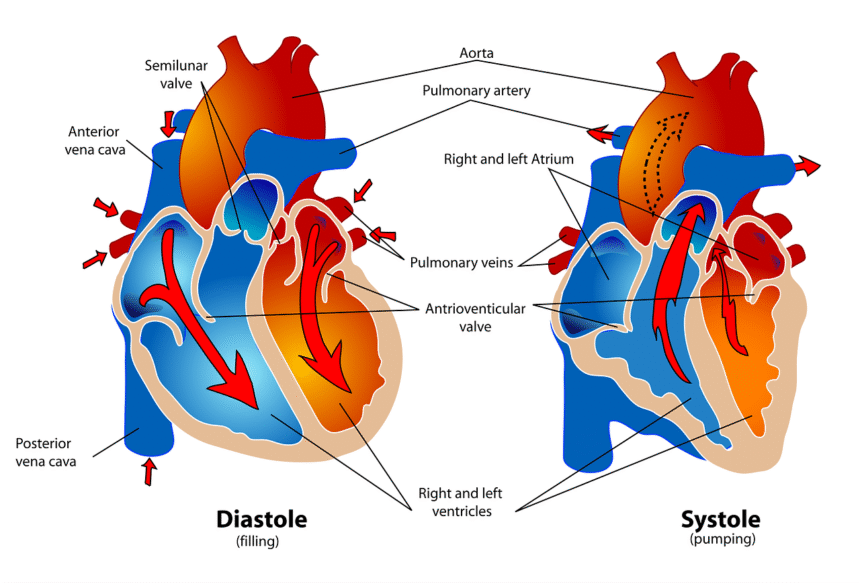
Healthcare systems significantly impact patient results by providing giving to high-quality care, professionals, and advanced medical technology. A strong system helps in early diagnosis, proper treatment, and better recovery rates.
Good healthcare systems also focus on patient safety, follow-up care, and support services. These factors together improve overall health, reduce hospital stays, and lower death rates, making the system essential for better patient outcomes and healthier communities.
Healthcare Systems of America
The healthcare system of America includes hospitals, clinics, doctors, insurance companies, and government programs. It offers both public and private healthcare services. People can get care through insurance plans like Medicare, Medicaid, or private coverage.
The system focuses on patient care, advanced treatments, and medical research. Although it provides high-quality services, costs can be high. Improving access and reducing costs are ongoing goals in the U.S. healthcare system.
Health System Membership
Health system membership helps patients get better, more connected care through a network of hospitals, clinics, and doctors. Members often receive coordinated services, faster support, and access to special programs.
Ira Byock, MD, FAAHPM, Chief Medical Officer at the Institute for Human Caring, Providence St. Joseph Health, supports improving care quality and making it more personal. His work helps health systems focus on compassion, comfort, and better patient experiences.
Hospital Membership
Health System Membership in the USA offers better care through trusted hospitals, clinics, and health experts. Members get easy access to services, regular check-ups, and care that fits their needs. Dr. Ira Byock, MD, FAAHPM, Chief Medical Officer at the Institute for Human Caring, Providence St. Joseph Health, supports this caring approach to improve lives.
Membership Types and Annual Fees
| Membership Type | Annual Fee |
| Individual Plan | $250/year |
| Family Plan (up to 4) | $600/year |
| Senior Plan (65+) | $200/year |
How to Contact Us
For more details or to join, please contact us:
- Phone: (800) 123-4567
- Email: info@healthmembershipusa.org
- Website: www.healthmembershipusa.org
Healthcare Systems Ranked
Healthcare systems are ranked means comparing different countries or states based on how well their healthcare works. Rankings look at things like patient care, cost, access, and health results.
In the USA, rankings help people understand which systems provide better services. These reports also help hospitals and professionals improve care. A high-ranking healthcare system usually means better patient safety, faster service, and more effective treatment for everyone.
Healthcare System Performance Rankings
Healthcare system performance rankings show how well different healthcare systems work in areas like patient care, access, safety, and cost. These rankings help people, hospitals, and governments see what’s working and what needs to improve.
In the USA, performance rankings guide decisions to make care better and more affordable. A higher ranking often means better patient outcomes, shorter wait times, and improved overall health in the community.
CEOWORLD Magazine’s Health Care Index 2024
According to the 2024 edition of the CEOWORLD Magazine Health Care Index, Taiwan is ranked as the country with the best healthcare system globally, with an overall score of 78.72.
South Korea follows in second place with a score of 77.7, and Australia ranks third with 74.11. This index evaluates 110 countries based on factors such as healthcare infrastructure, competencies of healthcare professionals, cost per capita, availability of quality medicine, and government readiness.
The ten countries with the best healthcare are:
- Taiwan (78.72)
- South Korea (77.7)
- Australia (74.11)
- Canada (71.32)
- Sweden (70.73)
- Ireland (67.99)
- Netherlands (65.38)
- Germany (64.66)
- Norway (64.63)
- Israel (61.73)
Source: CEOWORLD Magazine
Healthcare Systems Engineering
Healthcare Systems Engineering focuses on improving healthcare delivery by applying engineering principles to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve patient outcomes. This interdisciplinary field combines knowledge from engineering, healthcare, and management to optimize complicated healthcare systems.
Top Healthcare Systems Engineering Programs in the USA
Several esteemed institutions offer specialized programs in Healthcare Systems Engineering. Below is a selection of notable programs:
| Institution | Program Name | Tuition & Fees |
| Johns Hopkins University | MS in Healthcare Systems Engineering | Available upon request. |
| University of Southern California | MS in Health Systems Management Engineering | Available upon request. |
| Binghamton University | MS in Healthcare Systems Engineering | Total program fee: $38,000 |
| Lehigh University | Master of Engineering in Healthcare Systems | Available upon request. |
| Loyola Marymount University | MS in Healthcare Systems Engineering | Available upon request. |
These programs are designed to equip students with the skills necessary to address challenges in healthcare delivery through engineering solutions. Prospective students should review each program’s specific admission requirements and tuition details, as they may vary.
Healthcare Systems Near Me
Accessing healthcare in the USA involves understanding local healthcare systems and knowing how to find and schedule appointments with the right specialists. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you:
Understanding Local Healthcare Systems
In the USA, healthcare services are provided through a mix of public and private systems, including hospitals, clinics, and specialized care centers. Community health centers offer primary and preventive care, often serving underserved populations. Free clinics provide services to economically disadvantaged individuals at minimal or no cost.
Finding the Right Doctor or Specialist
To locate a suitable healthcare provider near you, consider the following resources:
- Zocdoc: Allows you to search for doctors by specialty and location, view real-time availability, and book appointments online.
- WebMD’s Physician Directory: Provides a searchable database of doctors by specialty and geographic area.
- Healthgrades: Offers comprehensive information on physicians, including patient reviews and ratings.
- American Medical Association (AMA) DoctorFinder: Provides information on virtually every licensed physician in the United States.
Scheduling an Appointment
Once you’ve identified a suitable doctor or specialist, scheduling an appointment can be done through:
- Online Platforms: Many healthcare providers offer online booking through their websites or patient portals.
- Third-Party Services: Platforms like Zocdoc facilitate online appointment scheduling.
- Phone Calls: Directly calling the doctor’s office remains a common method. Be prepared to provide your personal information, reason for the visit, and insurance details.
Tips for an Easy Appointment Process
- Verify Insurance Coverage: Ensure the provider accepts your insurance plan to avoid unexpected costs.
- Prepare Necessary Documents: Bring identification, insurance cards, and any relevant medical records.
- Arrive Early: Arriving 15 minutes before your scheduled time allows for check-in procedures.
By using these resources and tips, you can effectively navigate the healthcare system to find and schedule appointments with the appropriate specialists in your area.
Functions of a Health System: (WHO, 2000)
A health system is a group of people, organizations, and actions that work together to improve and protect public health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO, 2000), the main functions of a health system are to deliver quality healthcare services, build strong healthcare policies, develop and manage health resources like staff and equipment, and ensure financing is fair and efficient.
Health System Functions and Objectives (WHO, 2000):
| Functions of the Health System | Description |
| Service Delivery | Provide safe, high-quality, and accessible health care to all. |
| Health Workforce | Train and support skilled doctors, nurses, and other health professionals. |
| Health Information Systems | Collect and use data to plan and improve healthcare services. |
| Access to Medicines and Technology | Ensure the availability of essential medicines and medical equipment. |
| Health Financing | Secure fair funding so people can get care without financial hardship. |
| Leadership and Governance | Make strong policies and decisions that guide the health system. |
Objectives of a Health System (WHO, 2000)
| Objectives of a Health System (WHO, 2000) | Description |
| Improve Health of the Population | Help people live healthier and longer lives. |
| Enhance Responsiveness to People’s Needs | Make sure care is respectful, timely, and centered around patients. |
| Fair Financial Contribution | Protect people from high medical costs and financial stress. |
A well-functioning health system creates better health for everyone, supports communities, and builds trust between people and providers. These core functions and goals ensure that care is not just available—but also fair and effective.